Best Spam Checker For Email Tools To Boost Deliverability In 2026
In 2026, email deliverability remains one of the biggest challenges for marketers, sales teams, and businesses of all sizes — no matter how compelling your message is, it won’t matter if it ends up in the spam folder. Modern spam filters have evolved beyond basic keyword matching to evaluate everything from authentication protocols (like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC) to sender reputation, content quality, and engagement metrics.
To stay ahead, savvy senders are relying on advanced spam checker and deliverability tools that not only analyze your content and technical setup but also simulate real-world inbox placements across major providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo. These tools help pinpoint issues before campaigns are launched, offering actionable recommendations that directly improve inbox placement and campaign performance.
Whether you’re a solopreneur sending newsletters, a growth team scaling cold outreach, or a deliverability specialist managing complex drip campaigns, the right spam checker can dramatically boost your email deliverability — turning more opens into engagement and revenue. In this guide, we’ll explore the top spam checker tools in 2026 that are shaping how inbox placement is measured, optimized, and achieved.

Why spam checkers matter in 2026: Gmail/Yahoo sender requirements, privacy shifts, and deliverability impact
Gmail and Yahoo tightened sender requirements in recent years, and by 2026 those standards are table stakes. To keep email messages out of the spam folder, brands must pass authentication (SPF, DKIM, and DMARC), honor one-click unsubscribe, and hold complaint rates well below thresholds measured by Postmaster Tools and similar dashboards. A modern spam checker helps you operationalize these rules, turning policy into a concrete deliverability test you can run before you send emails at scale.
Privacy changes amplify the need. With mailbox providers obscuring opens and link events and browsers limiting third‑party cookies, you can’t rely on legacy tracking for health signals. A robust spam test and spam analysis fill the gap by detecting email spam risks earlier—before they trigger a spam filter. They score your email content, run a spam words list check, and surface authentication or infrastructure errors that quietly torpedo email deliverability and email reputation.
Finally, user expectations evolved. Recipients report and delete email messages faster when they see spammy words, urgency words, or unnatural words that overpromise. A proactive spam checker flags those spam trigger words and recommends how to remove spam words so your email campaign uses clear, trustworthy language. The payoff is fewer blocks, stronger sender reputation, and more predictable inbox placement across Gmail, Outlook, and other providers.
Stricter authentication and compliance
- Mandatory SPF check, DKIM check, and DMARC check for domains that send bulk emails or mass emails
- RFC‑compliant headers, working reply‑to email address, and list‑unsubscribe to avoid spam complaints
- Ongoing anti-spam enforcement using machine learning and human signals
Privacy shifts reduce data noise
- Less reliable open tracking means more emphasis on deliverability test workflows and inbox placement experiments
- Greater reliance on first‑party engagement and content quality instead of raw tracking
Deliverability impact you can measure
- Preflight spam score and spam test result catch issues that push email messages to the spam folder
- Automated deliverability report ties content, infrastructure, and reputation together so teams can avoid spam at the source

How email spam checker tools work: content heuristics, authentication audits, blocklist lookups, and inbox placement tests
Modern platforms combine content intelligence, infrastructure audits, and live tests to predict how a spam filter will treat your sends. The best spam checker solutions don’t just label—they prescribe fixes to remove spam words, repair alignment, and protect email deliverability across providers.
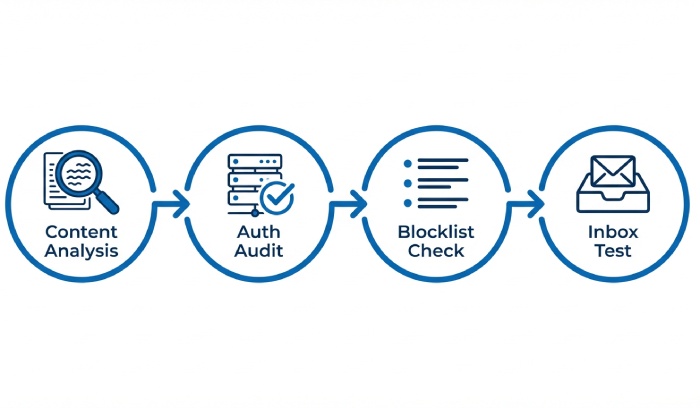
Content heuristics and language models
Advanced spam detection engines scan the email content—including subject lines, preheaders, and email templates—for risky phrasing. They weigh spam words and spam trigger words differently depending on context, looking for spammy words such as money words, overpromise claims, shady words, urgency words, and other patterns that correlate with email spam.
Building and maintaining a spam words list
- Continuously updated spam words list based on global provider feedback, complaint patterns, and anti-spam research
- Industry‑specific variants to reduce false positives and help you avoid spam without diluting your message
Context-aware detection of spam trigger words
- Models distinguish legitimate offers from manipulative copy, reducing flags for necessary terms
- Clear guidance to remove spam words or rewrite unnatural words while preserving personalization
Authentication and infrastructure audits
A good spam checker validates the technical layer that mailbox providers trust most.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC alignment checks
- Automated SPF check for record syntax and include chains
- DKIM check for key length, selectors, and alignment
- DMARC check for policy strength, alignment mode, and reporting
- Recommendations for enforcement, subdomain strategy, and BIMI preparedness to strengthen email reputation
Blocklist and reputation checks
Provider coverage matters. Tools run a blacklist checker across major DNSBLs, monitor ASN/IP/domain reputation, and evaluate sender reputation trends. They also run email validation and email address verification—complementary to email verification—to reduce hard bounces that degrade email deliverability.
Inbox placement and real-world experiments
Seed‑based deliverability test workflows place messages in controlled mailboxes to measure inbox placement vs. spam folder rates across Gmail, Outlook, and more. Many platforms support quick copy/paste email checks and a newsletter test mode so you can preview a newsletter spam test before a full send. Results feed into email scoring to create a composite spam score and a prescriptive deliverability report.
Evaluation criteria: accuracy, coverage by provider, AI-driven scoring, integrations, automation, security, and cost
Choosing a spam checker in 2026 means balancing technical depth with usability for marketers, developers, and ops.
Accuracy and provider coverage
- Depth of spam analysis and precision of spam score across Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and regional providers
- Breadth of blacklist checker sources and cadence of updates
- Quality of recommendations to remove spam words and repair authentication
AI-driven email scoring and explainability
- Transparent scoring that ties spam words, spam trigger words, and structure to risk, not just a number
- AI‑generated rewrite suggestions for email content that keep intent while avoiding unnatural words
- Optional AI Email Writer assistance for compliant drafts calibrated to anti-spam guidelines
Integrations, email API, and workflow automation
- Native connectors with Mailchimp, MailerLite, Lemlist, and an email campaign manager to test before launch
- Email API and automation hooks to run a spam test on every build, including follow-ups and sequences
- Tight loops with Google Sheets, Google Docs, Excel, and Gmail mail merge tools (e.g., Mailmeteor) so teams can personalize at scale without breaking compliance
Security, compliance, and cost
- Data handling that respects privacy laws, minimal storage of email messages, and enterprise-grade security
- Role-based access control and SSO for large teams trusted by professionals in regulated sectors
- Pricing aligned to volumes for bulk emails as well as flexible plans for small teams, with a clear free tool tier for ad‑hoc checks

2026 roundup of leading spam checker tools (examples and standout strengths)
Below are representative options that are widely used in 2026 for spam detection, authentication audits, and inbox placement testing.
Mailmeteor Spam Checker
Mailmeteor offers an accessible Spam Checker tightly integrated with its Gmail mail merge ecosystem. Standouts include:
- Content intelligence that flags spam words and spam trigger words with actionable rewrite tips to avoid spam
- Built‑in SPF check, DKIM check, and DMARC check with alignment guidance and a consolidated deliverability report
- Seamless use alongside Email Checker, Email Finder, Reverse Email Lookup, and Email Extractor for upstream list hygiene, plus Email Reputation dashboards
- Works where marketers live: Google Sheets add‑ons, Google Docs drafting, and Outlook compatibility; perfect for copy/paste email reviews and pre‑send newsletter test runs
- Extra utilities such as AI Email Writer for on‑brand edits, tracking options, and automation hooks to run a deliverability test before you send emails
mail-tester.com
mail-tester.com remains a popular free tool for quick checks. Strengths:
- Instant spam score with a transparent breakdown, easy copy/paste email testing, and a shareable spam test result
- Lightweight blacklist checker, SPF/DKIM/DMARC validation, and a clear path to remove spam words
- Great for small teams needing a fast newsletter spam test without complex setup
Mailchimp and MailerLite pre-send checks
If you run campaigns in an email campaign manager, the built‑in tests are convenient:
- Automated content checks for spam words, risky formatting, and broken links inside email templates
- Authentication diagnostics with domain connection wizards, email validation, and deliverability report snapshots
- Integrated with personalization, automation journeys, follow-ups, and tracking so compliance stays in flow

Lemlist deliverability suite
Lemlist focuses on sales outreach at scale:
- Pre‑send spam test with inbox placement seeds across major providers including Gmail
- Guidance to tune copy that may contain spammy words or urgency words often used in outbound email messages
- Reputation monitors for domains and IPs plus suggestions that historically overlapped with email warm-up practices; in 2026, emphasis is on compliant testing over automated warm-up
Developer-centric options (Postmark/Mailgun style checks and beyond)
For technical teams:
- API-first spam checker endpoints to gate deployments; ideal for CI pipelines via an email application programming interface(API)
- Detailed authentication analyzers and DNS inspectors, plus blacklist checker automation
- Programmatic email scoring and exportable deliverability report artifacts for audits
How to match tools to your workflow
- For marketers sending bulk emails and mass emails: choose a platform with strong UI, AI‑assisted rewrites, and deep provider coverage
- For sales teams: prioritize fast spam test feedback loops, personalization helpers, and safeguards against overpromise or shady words
- For developers: look for robust APIs, infrastructure diagnostics, and security posture appropriate for enterprise
Across these tools, the common thread is a disciplined preflight: run a deliverability test, audit authentication, scan the spam words list, and refine copy to remove spam words without losing voice. Done consistently, this practice curbs email spam, improves sender reputation, and keeps your campaigns out of the spam folder—protecting email deliverability when it matters most.
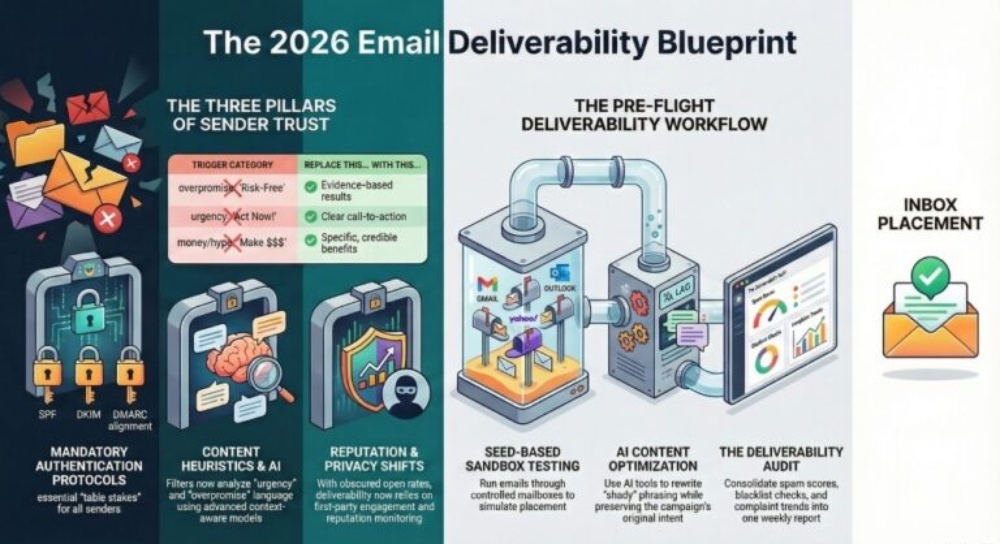
Interpreting spam scores: common triggers and how to fix copy, HTML, images, links, and attachments
How to read a spam score and prioritize fixes
A spam score summarizes how likely your email messages are to trigger an anti-spam rule or spam filter. Most spam checker tools break the spam test into categories—authentication, content, technical, and reputation—so you can triage issues. Start with high-impact items that push emails into the spam folder, then iterate on lower-weighted items affecting email deliverability marginally.
- Authentication and DNS issues typically contribute the largest penalties to your spam score.
- Content items like spam words and spam trigger words are next—fix these quickly to remove spam words and reduce risk.
- Technical HTML errors, broken links, and heavy images add up across your email content.
- Reputation signals (IP/domain, blacklist hits, spam complaints) compound the score and drag inbox placement down.
Run a deliverability test using a spam checker such as Mailmeteor’s Spam Checker, mail-tester.com (a widely used free tool trusted by professionals), or Nureply to evaluate how your emails are perceived by modern spam filters. Compare the spam test results against your baseline runs to identify improvements or regressions in authentication, content, and sender reputation. Document every change in a structured deliverability report so you can clearly track how each adjustment—whether technical or content-related—directly influences your overall email scoring and inbox placement over time.
Copy and language fixes that reduce content penalties
Copy is where most teams can quickly improve a spam score. Audit your subject line and body against a curated spam words list, and use a spam checker to highlight spammy words in context. Then:
- Remove spam words and replace them with plain, credible phrasing. Watch for overpromise phrases, urgency words, and money words that look like hype.
- Avoid unnatural words and shady words that read like clickbait; stick to clear benefits and proof.
- Calibrate personalization to add relevance without excessive merge tags that feel robotic.
Use an AI Email Writer to brainstorm alternatives, but always verify with a spam test and human editing. Keep email templates concise, minimize exclamation marks, and avoid ALL CAPS. When you must reference pricing or offers, soften the tone and add specifics to pass spam detection.

Language patterns most likely to trigger content filters
- Overpromise: guarantees, “risk-free,” or unbelievable results.
- Urgency words: “act now,” “don’t miss,” excessive countdowns.
- Money words: “cash,” “make $$$,” aggressive discount framing.
Replace with evidence-based statements, clear call-to-actions, and credible social proof to avoid spam while preserving conversions.
HTML and design hygiene that filters trust
Many spam filter engines penalize messy code. Keep HTML tight, standards-compliant, and mobile-first.
- Validate HTML/CSS; remove deprecated tags and inline styles that look like legacy spam.
- Maintain a healthy text-to-image ratio; include ALT text and live text for headlines.
- Avoid hidden text or mismatched font colors that resemble cloaking.
Leverage an email checker that runs a preflight QA on HTML weight, broken tags, and tracking pixels. When possible, use modern, lightweight email templates from reputable providers (Mailchimp, MailerLite, Lemlist) and re-run a deliverability test after modifications.
Links, images, and attachments: safe defaults
- Link reputation: Ensure the display domain matches the destination domain; avoid URL shorteners. Track clicks, but host redirects on your own domain.
- Images: Compress and host on HTTPS; avoid image-only email messages. Excessive image weight hurts email deliverability.
- Attachments: Prefer links to hosted files. If you must attach, use common formats and small sizes.
Check links in a seed inbox across Gmail and Outlook to confirm rendering, and rerun a spam test to see if link changes improved your spam score.
Authentication and reputation essentials: SPF, DKIM, DMARC alignment, BIMI, TLS, and feedback loops

Alignment basics: SPF, DKIM, DMARC done right
Authentication failures are a primary driver of email spam placement. Implement:
- SPF with strict include mechanisms and an SPF check to confirm authorized senders.
- DKIM signing on all send domains; run a DKIM check on test emails.
- DMARC policy with alignment; start at p=none, review reports, then move to quarantine/reject. Use a DMARC check to verify alignment.
Strong alignment boosts email reputation and helps anti-spam systems trust your email messages. Add ARC only if your flows route through intermediaries that might break alignment.
Visual trust and transport security: BIMI and TLS
- BIMI displays a verified brand logo in supporting inboxes after you meet DMARC enforcement and obtain a VMC. While cosmetic, BIMI can increase engagement and reduce spam folder risk indirectly.
- Enforce Transport Layer Security(TLS) for transport encryption and prefer modern ciphers. Some spam filters score down unencrypted hops.
Feedback loops and ongoing sender reputation
Enroll in ISP feedback loops to capture complaints. Monitor complaint rates, blacklist checker statuses, and blocklist incidents to protect email reputation. If reputation dips, execute an email warm-up and reduce volume until inbox placement stabilizes.
Proven testing workflows: seed lists, panel data, pre-send checks, and ongoing deliverability monitoring
Pre-send checks with seed lists and sandbox tools
Before you send emails at scale, run a deliverability test to multiple seed mailboxes. Include Gmail, Outlook, and regional providers. Use mail-tester.com for a quick spam test and email scoring snapshot, then compare with Mailmeteor’s Spam Checker for deeper spam analysis and a structured spam words list review. For newsletters, run a newsletter test or newsletter spam test on the final creative.
- Copy/paste email into a sandbox spam checker to spot spam trigger words instantly.
- Validate authentication with automated SPF check, DKIM check, and DMARC check.
- Confirm links, tracking, and images render correctly.
Panel data and inbox placement tracking
Augment seed tests with panel-based inbox placement data to see where real users receive your email campaign—Primary, Promotions, or spam folder. Track changes in spam folder rate across segments, and correlate with content, cadence, and sender reputation adjustments.
Monitoring, alerting, and deliverability reports
Create a weekly deliverability report that consolidates spam test result history, blocklist hits from a blacklist checker, complaint trends, opens/clicks, and bounce diagnostics. Automate alerts when spam score thresholds are exceeded so you can remove spam words, adjust cadence, or pause bulk emails before damage spreads.
Integrations and automation: connecting spam checks to ESPs, CRMs, CI/CD, and approval workflows
ESP and CRM hookups for frictionless QA
Integrate your spam checker with Mailchimp, MailerLite, Lemlist, and Gmail to run pre-send checks directly inside your email campaign manager. Pull drafts straight from your ESP, run a deliverability test, and push fixes back to your email templates before sending. Sync deliverability results to your CRM so sales teams can see risk flags before follow-ups and adjust messaging, timing, or authentication settings—ensuring every follow-up email is just as optimized for inbox placement as the initial send.
- Mailmeteor integrates with Google Sheets and Google Docs for content ops; use add-ons to score copy, remove spam words, and standardize templates.
- For Outlook and Excel workflows, export a deliverability report for stakeholder review.
CI/CD, email API, and content governance
Treat templates like code. In CI/CD, lint HTML, run a spam test via email API, and fail the build if the spam score exceeds a threshold or if spam detection flags high-risk language. Automate SPF/DKIM/DMARC validation on domain changes, and gate releases on passing checks.
Approvals, mail merge, and productivity tools
Build an approval workflow: writer > peer review > spam checker > legal > send. For mail merge, connect Gmail mail merge to run spam analysis on variants before bulk sends. Leverage Mailmeteor’s AI Email Writer, Email Checker, Email Finder, Reverse Email Lookup, and Email Extractor to keep email address verification, targeting, and personalization clean while protecting Email Reputation.
Unifying checks across the toolchain
- Run email verification and email validation on lists.
- Score drafts automatically, highlight spammy words, and suggest alternatives.
- Push final tests to seed lists and archive results for audit.

Implementation roadmap and KPIs: rollout steps, baselines, remediation, and continuous optimization
Rollout steps and baseline definition
1) Audit domains: SPF, DKIM, DMARC alignment, TLS, BIMI readiness.
2) Establish baselines: current spam score ranges, spam folder placement, bounce rates, and complaint rates.
3) Implement a spam checker in staging; require deliverability test passes before bulk emails.
4) Train teams on the spam words list and how to remove spam words during copy reviews.
5) Launch monitoring with alerts and a recurring deliverability report.
Include list hygiene with email address verification and periodic email validation to protect sender reputation.
KPIs that predict inbox placement
- Spam score thresholds by segment and template type.
- Inbox placement and spam folder rates across Gmail and other ISPs.
- Complaint rate, blocklist incidents, and blacklist checker findings.
- Engagement trends post-remediation (opens, clicks, conversions).
Use tracking to correlate changes, and document remediation impact in a deliverability report that leadership can review.
Remediation and continuous optimization
If performance degrades, pause mass emails, reduce cadence, and run a root-cause analysis. Remove spam words, refactor email content, and retest. Improve authentication, repair links, and refresh segments. After incidents, complete an email warm-up cycle and gradually scale volume. Maintain a living spam words list, keep anti-spam practices current, and iterate templates to avoid spam across every email campaign.

FAQs
What is a good spam score before sending a campaign?
Aim for a low or “passing” spam score in your spam checker, with no critical authentication or content issues. Combine this with a deliverability test to seed inboxes to confirm inbox placement before sending bulk emails.
How often should I run a spam test?
Run a spam test for every major campaign and whenever you change templates, domains, or tracking. Ongoing tests catch regressions early and prevent email messages from drifting into the spam folder.
Do attachments hurt email deliverability?
Attachments can increase your spam score and trigger spam filters. Prefer hosted files behind reputable, HTTPS links and retest to ensure anti-spam systems accept your email content.
Which authentication settings matter most?
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC alignment are foundational; verify with SPF check, DKIM check, and DMARC check. Strengthen with TLS and consider BIMI after DMARC enforcement for added trust.

How do I deal with spam words without losing conversions?
Replace spammy words and spam trigger words with specific, evidence-based phrasing. Use a spam words list, remove spam words, and retest copy until you pass both the spam checker and engagement benchmarks.
What tools should I use for testing and monitoring?
Combine mail-tester.com for quick scoring with a platform like Mailmeteor’s Spam Checker for workflow integration, alerts, and reporting. Add a blacklist checker and panel-based inbox placement to round out your deliverability report.
Can I automate checks inside my ESP or CRM?
Yes. Connect your spam checker via email API or native integrations to Mailchimp, MailerLite, Lemlist, or Gmail. Automate preflight checks, approvals, and alerts as part of your CI/CD and campaign workflows.
Key Takeaways
- Treat authentication, content quality, and reputation as equal pillars of email deliverability; test them before every send.
- Use a spam checker to find spam words, fix HTML and links, and reduce your spam score, then verify with seed lists and panel data.
- Institutionalize workflows: CI/CD checks, approvals, alerts, and deliverability reports to catch issues before bulk emails go out.
- Integrate with ESPs and CRMs, automate SPF/DKIM/DMARC checks, and keep a living spam words list to avoid spam long term.
- Monitor KPIs—spam folder rate, inbox placement, sender reputation—and remediate quickly with testing and list hygiene.







